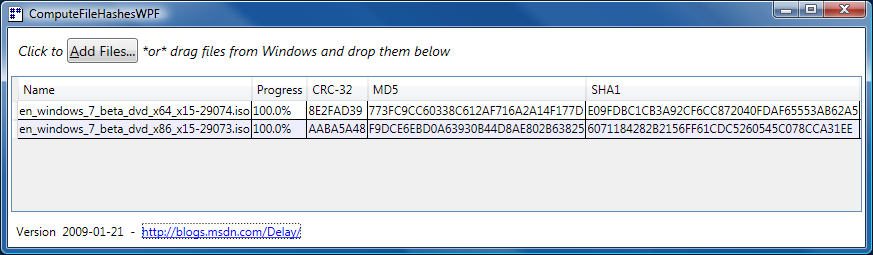
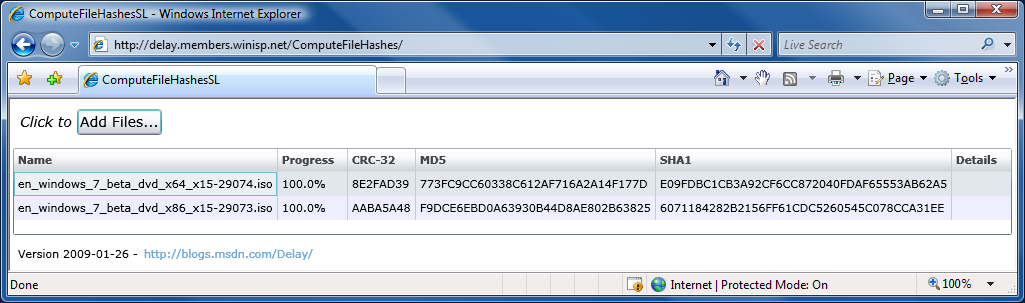
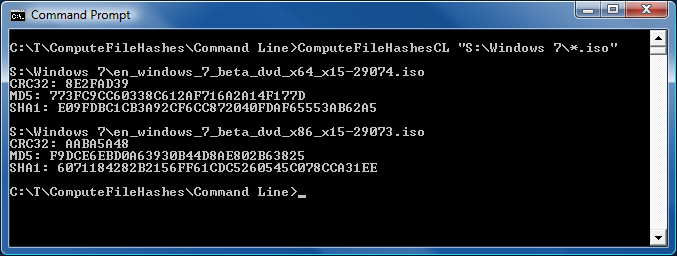
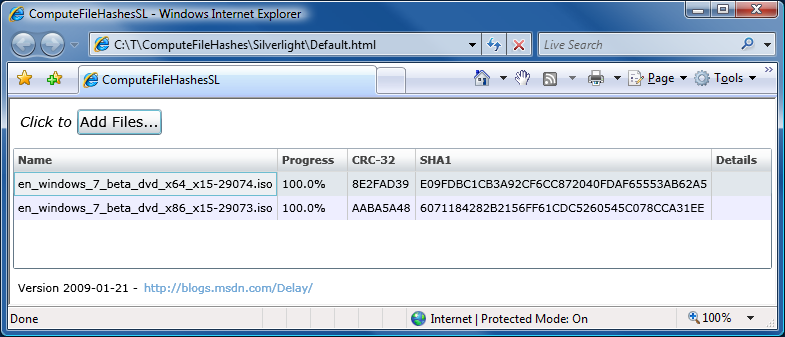
Thank goodness for reference implementations [Low-overhead .NET MD5 implementation (source code and tests) works great on Silverlight!]
In yesterday's post announcing ComputeFileHashes's new support for MD5 on Silverlight, I promised to share some details about my experience getting an MD5 HashAlgorithm implementation for Silverlight. Recall that an MD5 class is available in the desktop .NET Framework, but is not part of Silverlight 2's subset of the .NET Framework. (Probably in order to save space by excluding one of the less-secure cryptographic hash functions - a completely sensible tradeoff.) Because I didn't want to write my own code for MD5 (it's a non-trivial algorithm), the challenge was to find something freely available that I could just drop in and take advantage of. So I was very interested when I found out about Reid Borsuk's managed implementation of an MD5 HashAlgorithm for Silverlight because it sounded perfect for my needs.
The first step of incorporating something like this is to check the license: this code is under Ms-PL, so there were no problems there. The next step is to skim the code and get a general feel for how it works - and it was while doing this that I realized I wouldn't be able to use this code as-is...
To understand why, a little background is required:
The HashAlgorithm abstract class requires that derived classes implement the following methods: Initialize, HashCore, and HashFinal. Initialize gets called once at the start of hashing, then HashCore is called many times (being passed a different block of data each time), and then HashFinal is called once at the end of hashing to finalize any computations and return the computed hash value. It's a straightforward model and is flexible enough to accommodate a wide variety of checksum algorithms. Other than maintaining a few bytes of internal state across calls, there's no need for the hash algorithm to allocate anything: the data flows in from the user, gets processed, and is immediately forgotten about.
Or at least that's how it's supposed to work...
What I found when I looked at the aforementioned MD5 implementation was that it would allocate an internal buffer during Initialize, repeatedly re-allocate that buffer and append new data to the end of it during every call to HashCore, and then process the entire buffer all at once in HashFinal. While this approach works fine for fairly small inputs, it was completely impractical for ComputeFileHashes which is expected to process multi-gigabyte files as a matter of course. All those reallocations and the large internal buffer would quickly exhaust the physical memory of virtually any system in use today on something like the Windows 7 Beta ISO images I've been using for my examples. (In fact, it's a bit more dire than it initially seems: this technique requires twice the memory of the original data: that last call to HashCore needs to copy the nearly-full-sized buffer into a new full-sized buffer.)
Okay, so if I couldn't use the code as-is; the next step is to see what it would take to modify it so that it would work for my scenario. Well, this implementation uses a small HashAlgorithm wrapper class around a core MD5 implementation class, I wondered if it would be a simple matter of changing the way the wrapper called into the core. But looking at things a bit more closely, it seemed the core was not structured for that - and separating things like I wanted might not be trivial.
It's decision time: Do I start changing the structure of this code to work the way I need it to, or do I investigate other options? I considered the implications of both approaches, but it was something a coworker said that convinced me to spend a bit of time looking elsewhere. He asked, "If you don't like a fundamental part of the implementation and feel the need to fix it, why do you think you won't be compelled to make changes to the rest of it as well?" That question expressed my concerns pretty well, so I decided to look into other options for a bit. After all, I could always come back to this if nothing panned out.
The obvious place to start was the MD5 specification: RFC1321, The MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm. The body of this document describes the algorithm in great detail and would be a great place to start writing my own implementation if I was willing to spend a considerable amount of time developing and testing. But the real gem is in the appendix: a reference implementation of MD5 written in C! Fortunately, C's not so different from C# - and I've ported things before - so I had a decent idea what to expect. And it sure is hard to beat the reference implementation from the point of view of obtaining an accurate, (typically) bug-free, chunk of code. There is an accompanying license, but it's open (this is a public specification, after all) and primarily requires that derivative works identify themselves as being "derived from the RSA Data Security, Inc. MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm." (like I just did). So things seemed promising!
I decided to spend a bus ride porting the reference implementation and see how far I got. As it happens (and I'm sure this is no accident), the reference implementation uses exactly the Initialize/HashCore/HashFinal pattern that HashAlgorithm expects. Consequently, each of my own HashAlgorithm wrapper methods simply makes a single call into the ported reference implementation - and all of a sudden concerns about memory exhaustion are a thing of the past! By the end of the bus ride, I had successfully ported the reference implementation to C# and had it passing the seven test cases that are part of the specification.
My mind was pretty much made up at this point: I'd use my port of the MD5 reference implementation for the Silverlight version of ComputeFileHashes. This was code from a reliable source, code I had become familiar with, and code that I'd feel comfortable debugging or tuning if necessary. I beefed up the test cases a bit by exercising all of them for all the possible chunk sizes, addressed a couple of code analysis warnings, and had something ready in a jiffy. I added the MD5Managed class to the Silverlight build of ComputeFileHashes and - yep - it just worked. :)
So here's a(nother) completely managed MD5 implementation that anyone is free to use (subject to the reference implementation's license). I haven't spent time optimizing it - but that was kind of the point (see the class comments below for more). I'd started out trying to avoid writing my own MD5 implementation and I only partly succeeded - but I'm glad with how this worked out and maybe some of you can benefit from what I've done. Even if all you do is run the Silverlight version of ComputeFileHashes from time to time, I feel like my relatively minimal investment was worthwhile! :)
using System; using System.Diagnostics.CodeAnalysis; using System.Security.Cryptography; namespace Delay { /// <summary> /// MD5Managed: A HashAlgorithm implementation that acts as a thin wrapper /// around a C# translation of the MD5 reference implementation. The C code /// has been translated as closely as possible so that most of the original /// structure remains and comparisons between the two are straightforward. /// </summary> /// <remarks> /// Derived from the RSA Data Security, Inc. MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm. /// /// Specification: /// RFC1321 - The MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm /// http://www.faqs.org/rfcs/rfc1321.html /// /// Original license: /// Copyright (C) 1991-2, RSA Data Security, Inc. Created 1991. All /// rights reserved. /// /// License to copy and use this software is granted provided that it /// is identified as the "RSA Data Security, Inc. MD5 Message-Digest /// Algorithm" in all material mentioning or referencing this software /// or this function. /// /// License is also granted to make and use derivative works provided /// that such works are identified as "derived from the RSA Data /// Security, Inc. MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm" in all material /// mentioning or referencing the derived work. /// /// RSA Data Security, Inc. makes no representations concerning either /// the merchantability of this software or the suitability of this /// software for any particular purpose. It is provided "as is" /// without express or implied warranty of any kind. /// /// These notices must be retained in any copies of any part of this /// documentation and/or software. /// </remarks> public class MD5Managed : HashAlgorithm { // Current context private readonly MD5_CTX _context = new MD5_CTX(); // Last hash result private readonly byte[] _digest = new byte[16]; // True if HashCore has been called private bool _hashCoreCalled; // True if HashFinal has been called private bool _hashFinalCalled; /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance. /// </summary> public MD5Managed() { InitializeVariables(); } /// <summary> /// Initializes internal state. /// </summary> public override void Initialize() { InitializeVariables(); } /// <summary> /// Initializes variables. /// </summary> private void InitializeVariables() { MD5Init(_context); _hashCoreCalled = false; _hashFinalCalled = false; } /// <summary> /// Updates the hash code with the data provided. /// </summary> /// <param name="array">Data to hash.</param> /// <param name="ibStart">Start position.</param> /// <param name="cbSize">Number of bytes.</param> protected override void HashCore(byte[] array, int ibStart, int cbSize) { if (null == array) { throw new ArgumentNullException("array"); } if (_hashFinalCalled) { throw new CryptographicException("Hash not valid for use in specified state."); } _hashCoreCalled = true; MD5Update(_context, array, (uint)ibStart, (uint)cbSize); } /// <summary> /// Finalizes the hash code and returns it. /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> protected override byte[] HashFinal() { _hashFinalCalled = true; MD5Final(_digest, _context); return Hash; } /// <summary> /// Returns the hash as an array of bytes. /// </summary> [SuppressMessage("Microsoft.Design", "CA1065:DoNotRaiseExceptionsInUnexpectedLocations", Justification = "Matching .NET behavior by throwing here.")] [SuppressMessage("Microsoft.Usage", "CA2201:DoNotRaiseReservedExceptionTypes", Justification = "Matching .NET behavior by throwing NullReferenceException.")] public override byte[] Hash { get { if (!_hashCoreCalled) { throw new NullReferenceException(); } if (!_hashFinalCalled) { // Note: Not CryptographicUnexpectedOperationException because that can't be instantiated on Silverlight 4 throw new CryptographicException("Hash must be finalized before the hash value is retrieved."); } return _digest; } } // Return size of hash in bits. public override int HashSize { get { return _digest.Length * 8; } } /////////////////////////////////////////////// // MD5 reference implementation begins here. // /////////////////////////////////////////////// /* MD5 context. */ private class MD5_CTX { public readonly uint[] state; /* state (ABCD) */ public readonly uint[] count; /* number of bits, modulo 2^64 (lsb first) */ public readonly byte[] buffer; /* input buffer */ public MD5_CTX() { state = new uint[4]; count = new uint[2]; buffer = new byte[64]; } public void Clear() { Array.Clear(state, 0, state.Length); Array.Clear(count, 0, count.Length); Array.Clear(buffer, 0, buffer.Length); } } /* Constants for MD5Transform routine. */ private const int S11 = 7; private const int S12 = 12; private const int S13 = 17; private const int S14 = 22; private const int S21 = 5; private const int S22 = 9; private const int S23 = 14; private const int S24 = 20; private const int S31 = 4; private const int S32 = 11; private const int S33 = 16; private const int S34 = 23; private const int S41 = 6; private const int S42 = 10; private const int S43 = 15; private const int S44 = 21; private static byte[] PADDING; [SuppressMessage("Microsoft.Performance", "CA1810:InitializeReferenceTypeStaticFieldsInline", Justification = "More compact this way")] static MD5Managed() { PADDING = new byte[64]; PADDING[0] = 0x80; } /* F, G, H and I are basic MD5 functions. */ private static uint F(uint x, uint y, uint z) { return (((x) & (y)) | ((~x) & (z))); } private static uint G(uint x, uint y, uint z) { return (((x) & (z)) | ((y) & (~z))); } private static uint H(uint x, uint y, uint z) { return ((x) ^ (y) ^ (z)); } private static uint I(uint x, uint y, uint z) { return ((y) ^ ((x) | (~z))); } /* ROTATE_LEFT rotates x left n bits. */ private static uint ROTATE_LEFT(uint x, int n) { return (((x) << (n)) | ((x) >> (32 - (n)))); } /* FF, GG, HH, and II transformations for rounds 1, 2, 3, and 4. Rotation is separate from addition to prevent recomputation. */ private static void FF(ref uint a, uint b, uint c, uint d, uint x, int s, uint ac) { (a) += F((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (uint)(ac); (a) = ROTATE_LEFT((a), (s)); (a) += (b); } private static void GG(ref uint a, uint b, uint c, uint d, uint x, int s, uint ac) { (a) += G((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (uint)(ac); (a) = ROTATE_LEFT((a), (s)); (a) += (b); } private static void HH(ref uint a, uint b, uint c, uint d, uint x, int s, uint ac) { (a) += H((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (uint)(ac); (a) = ROTATE_LEFT((a), (s)); (a) += (b); } private static void II(ref uint a, uint b, uint c, uint d, uint x, int s, uint ac) { (a) += I((b), (c), (d)) + (x) + (uint)(ac); (a) = ROTATE_LEFT((a), (s)); (a) += (b); } /* MD5 initialization. Begins an MD5 operation, writing a new context. */ private static void MD5Init(MD5_CTX context) /* context */ { context.count[0] = context.count[1] = 0; /* Load magic initialization constants. */ context.state[0] = 0x67452301; context.state[1] = 0xefcdab89; context.state[2] = 0x98badcfe; context.state[3] = 0x10325476; } /* MD5 block update operation. Continues an MD5 message-digest operation, processing another message block, and updating the context. */ private static void MD5Update(MD5_CTX context, /* context */ byte[] input, /* input block */ uint inputIndex, // Starting index for input block uint inputLen) /* length of input block */ { /* Compute number of bytes mod 64 */ uint index = (uint)((context.count[0] >> 3) & 0x3F); /* Update number of bits */ if ((context.count[0] += ((uint)inputLen << 3)) < ((uint)inputLen << 3)) { context.count[1]++; } context.count[1] += ((uint)inputLen >> 29); uint partLen = 64 - index; /* Transform as many times as possible. */ uint i = 0; if (inputLen >= partLen) { Buffer.BlockCopy(input, (int)inputIndex, context.buffer, (int)index, (int)partLen); MD5Transform(context.state, context.buffer, 0); for (i = partLen; i + 63 < inputLen; i += 64) { MD5Transform(context.state, input, inputIndex + i); } index = 0; } /* Buffer remaining input */ Buffer.BlockCopy(input, (int)(inputIndex + i), context.buffer, (int)index, (int)(inputLen - i)); } /* MD5 finalization. Ends an MD5 message-digest operation, writing the the message digest and zeroizing the context. */ private static void MD5Final(byte[] digest, /* message digest */ MD5_CTX context) /* context */ { byte[] bits = new byte[8]; /* Save number of bits */ Encode(bits, context.count, 8); /* Pad out to 56 mod 64. */ uint index = (uint)((context.count[0] >> 3) & 0x3f); uint padLen = (index < 56) ? (56 - index) : (120 - index); MD5Update(context, PADDING, 0, padLen); /* Append length (before padding) */ MD5Update(context, bits, 0, 8); /* Store state in digest */ Encode(digest, context.state, 16); /* Zeroize sensitive information. */ context.Clear(); } /* MD5 basic transformation. Transforms state based on block. */ private static void MD5Transform(uint[] state, byte[] block, uint blockIndex) { uint a = state[0], b = state[1], c = state[2], d = state[3]; uint[] x = new uint[16]; Decode(x, block, blockIndex, 64); /* Round 1 */ FF(ref a, b, c, d, x[0], S11, 0xd76aa478); /* 1 */ FF(ref d, a, b, c, x[1], S12, 0xe8c7b756); /* 2 */ FF(ref c, d, a, b, x[2], S13, 0x242070db); /* 3 */ FF(ref b, c, d, a, x[3], S14, 0xc1bdceee); /* 4 */ FF(ref a, b, c, d, x[4], S11, 0xf57c0faf); /* 5 */ FF(ref d, a, b, c, x[5], S12, 0x4787c62a); /* 6 */ FF(ref c, d, a, b, x[6], S13, 0xa8304613); /* 7 */ FF(ref b, c, d, a, x[7], S14, 0xfd469501); /* 8 */ FF(ref a, b, c, d, x[8], S11, 0x698098d8); /* 9 */ FF(ref d, a, b, c, x[9], S12, 0x8b44f7af); /* 10 */ FF(ref c, d, a, b, x[10], S13, 0xffff5bb1); /* 11 */ FF(ref b, c, d, a, x[11], S14, 0x895cd7be); /* 12 */ FF(ref a, b, c, d, x[12], S11, 0x6b901122); /* 13 */ FF(ref d, a, b, c, x[13], S12, 0xfd987193); /* 14 */ FF(ref c, d, a, b, x[14], S13, 0xa679438e); /* 15 */ FF(ref b, c, d, a, x[15], S14, 0x49b40821); /* 16 */ /* Round 2 */ GG(ref a, b, c, d, x[1], S21, 0xf61e2562); /* 17 */ GG(ref d, a, b, c, x[6], S22, 0xc040b340); /* 18 */ GG(ref c, d, a, b, x[11], S23, 0x265e5a51); /* 19 */ GG(ref b, c, d, a, x[0], S24, 0xe9b6c7aa); /* 20 */ GG(ref a, b, c, d, x[5], S21, 0xd62f105d); /* 21 */ GG(ref d, a, b, c, x[10], S22, 0x02441453); /* 22 */ GG(ref c, d, a, b, x[15], S23, 0xd8a1e681); /* 23 */ GG(ref b, c, d, a, x[4], S24, 0xe7d3fbc8); /* 24 */ GG(ref a, b, c, d, x[9], S21, 0x21e1cde6); /* 25 */ GG(ref d, a, b, c, x[14], S22, 0xc33707d6); /* 26 */ GG(ref c, d, a, b, x[3], S23, 0xf4d50d87); /* 27 */ GG(ref b, c, d, a, x[8], S24, 0x455a14ed); /* 28 */ GG(ref a, b, c, d, x[13], S21, 0xa9e3e905); /* 29 */ GG(ref d, a, b, c, x[2], S22, 0xfcefa3f8); /* 30 */ GG(ref c, d, a, b, x[7], S23, 0x676f02d9); /* 31 */ GG(ref b, c, d, a, x[12], S24, 0x8d2a4c8a); /* 32 */ /* Round 3 */ HH(ref a, b, c, d, x[5], S31, 0xfffa3942); /* 33 */ HH(ref d, a, b, c, x[8], S32, 0x8771f681); /* 34 */ HH(ref c, d, a, b, x[11], S33, 0x6d9d6122); /* 35 */ HH(ref b, c, d, a, x[14], S34, 0xfde5380c); /* 36 */ HH(ref a, b, c, d, x[1], S31, 0xa4beea44); /* 37 */ HH(ref d, a, b, c, x[4], S32, 0x4bdecfa9); /* 38 */ HH(ref c, d, a, b, x[7], S33, 0xf6bb4b60); /* 39 */ HH(ref b, c, d, a, x[10], S34, 0xbebfbc70); /* 40 */ HH(ref a, b, c, d, x[13], S31, 0x289b7ec6); /* 41 */ HH(ref d, a, b, c, x[0], S32, 0xeaa127fa); /* 42 */ HH(ref c, d, a, b, x[3], S33, 0xd4ef3085); /* 43 */ HH(ref b, c, d, a, x[6], S34, 0x04881d05); /* 44 */ HH(ref a, b, c, d, x[9], S31, 0xd9d4d039); /* 45 */ HH(ref d, a, b, c, x[12], S32, 0xe6db99e5); /* 46 */ HH(ref c, d, a, b, x[15], S33, 0x1fa27cf8); /* 47 */ HH(ref b, c, d, a, x[2], S34, 0xc4ac5665); /* 48 */ /* Round 4 */ II(ref a, b, c, d, x[0], S41, 0xf4292244); /* 49 */ II(ref d, a, b, c, x[7], S42, 0x432aff97); /* 50 */ II(ref c, d, a, b, x[14], S43, 0xab9423a7); /* 51 */ II(ref b, c, d, a, x[5], S44, 0xfc93a039); /* 52 */ II(ref a, b, c, d, x[12], S41, 0x655b59c3); /* 53 */ II(ref d, a, b, c, x[3], S42, 0x8f0ccc92); /* 54 */ II(ref c, d, a, b, x[10], S43, 0xffeff47d); /* 55 */ II(ref b, c, d, a, x[1], S44, 0x85845dd1); /* 56 */ II(ref a, b, c, d, x[8], S41, 0x6fa87e4f); /* 57 */ II(ref d, a, b, c, x[15], S42, 0xfe2ce6e0); /* 58 */ II(ref c, d, a, b, x[6], S43, 0xa3014314); /* 59 */ II(ref b, c, d, a, x[13], S44, 0x4e0811a1); /* 60 */ II(ref a, b, c, d, x[4], S41, 0xf7537e82); /* 61 */ II(ref d, a, b, c, x[11], S42, 0xbd3af235); /* 62 */ II(ref c, d, a, b, x[2], S43, 0x2ad7d2bb); /* 63 */ II(ref b, c, d, a, x[9], S44, 0xeb86d391); /* 64 */ state[0] += a; state[1] += b; state[2] += c; state[3] += d; /* Zeroize sensitive information. */ Array.Clear(x, 0, x.Length); } /* Encodes input (UINT4) into output (unsigned char). Assumes len is a multiple of 4. */ private static void Encode(byte[] output, uint[] input, uint len) { for (uint i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i++, j += 4) { output[j] = (byte)(input[i] & 0xff); output[j + 1] = (byte)((input[i] >> 8) & 0xff); output[j + 2] = (byte)((input[i] >> 16) & 0xff); output[j + 3] = (byte)((input[i] >> 24) & 0xff); } } /* Decodes input (unsigned char) into output (UINT4). Assumes len is a multiple of 4. */ private static void Decode(uint[] output, byte[] input, uint inputIndex, uint len) { for (uint i = 0, j = 0; j < len; i++, j += 4) { output[i] = ((uint)input[inputIndex + j]) | (((uint)input[inputIndex + j + 1]) << 8) | (((uint)input[inputIndex + j + 2]) << 16) | (((uint)input[inputIndex + j + 3]) << 24); } } } }
Updated 2009-02-16: Call MD5Init from the constructor for consistency with the Framework's HashAlgorithm classes where a call to Initialize is not necessary for a newly constructed instance.
Updated 2010-12-06: Added missing inputIndex offset to MD5Update method.